Introduction
Supervised and Unsupervised learning are techniques in machine learning.
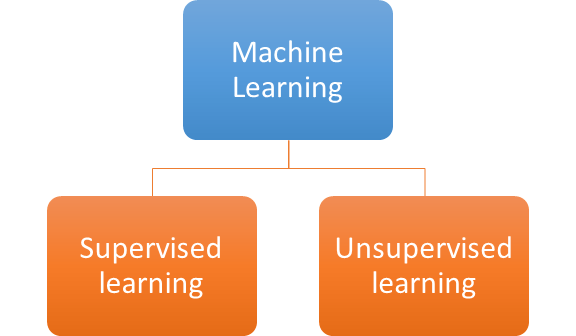
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning the input variables/attributes/features (X) and the output variables (Y) are given and the machine finds an optimal function to generalize through all the inputs . In very generic terms we can represent this as Y = f(X).
The machine trains on the training data and learns the patterns from this data set to predict the output of an unknown labelled data set.
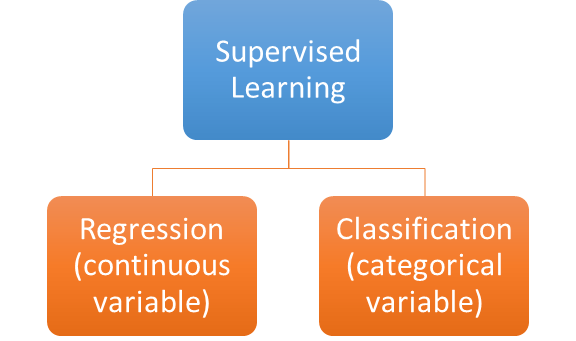
- Regression: The output label is continuous and can have any value. Example: temperature, weight etc.
- Some regression algorithms are:
- Linear regression
- Logistic regression
- Multivariate regression
- Lasso regression
- Ridge regression
- Some regression algorithms are:
- Classification: The output label is a finite set of categories or known values. Example: color(R, B, G), survived or not? country name etc.
- Some classification algorithms are:
- K- Nearest Neighbors( KNN)
- Decision tree
- Random Forest
- Naive Bayes
- Support Vector Classification (SVC)
- Some classification algorithms are:
Unsupervised Learning
The input data provided for training only contains the attributes/features (X) and does not contain any output labels/variables for prediction. Since there is no value/category for prediction the machine needs to find patterns/rules within the data set.
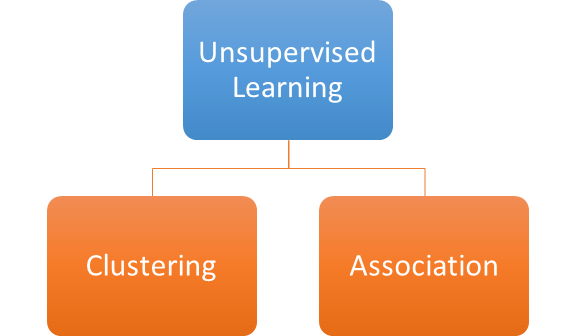
- Clustering : Discovers groups/clusters from a provided data set. Example : new music genre, unknown customer types based on purchasing patterns etc. K- Means algorithm is a common type of clustering algorithm.
- Association : Discover rules/ associations in the data set to help make decisions. Like this section of customers would purchase the product Y would also purchase the product Z. Common association algorithm is the Apriori algorithm for rule based learning.
Summary
