Introduction
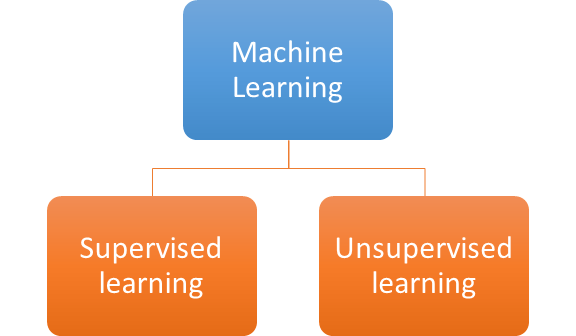
Supervised and Unsupervised learning are techniques in machine learning.
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning the input variables/attributes/features (X) and the output variables (Y) are given and the machine finds an optimal function to generalize through all the inputs . In very generic terms we can represent this as Y = f(X).
The machine trains on the training data and learns the patterns from this data set to predict the output of an unknown labelled data set.
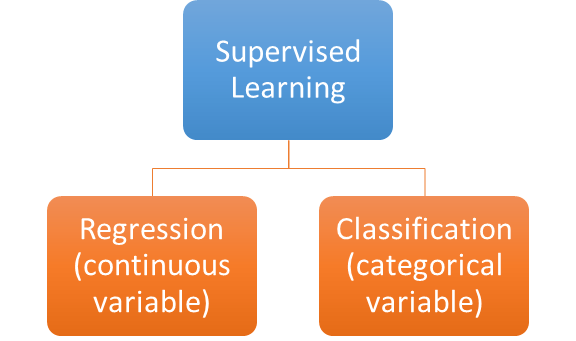
- Regression: The output label is continuous and can have any value. Example: temperature, weight etc.
- Some regression algorithms are:
- Linear regression
- Logistic regression
- Multivariate regression
- Lasso regression
- Ridge regression
- Some regression algorithms are:
- Classification: The output label is a finite set of categories or known values. Example: color(R, B, G), survived or not? country name etc.
- Some classification algorithms are:
- K- Nearest Neighbors( KNN)
- Decision tree
- Random Forest
- Naive Bayes
- Support Vector Classification (SVC)
- Some classification algorithms are:
Unsupervised Learning
The input data provided for training only contains the attributes/features (X) and does not contain any output labels/variables for prediction. Since there is no value/category for prediction the machine needs to find patterns/rules within the data set.
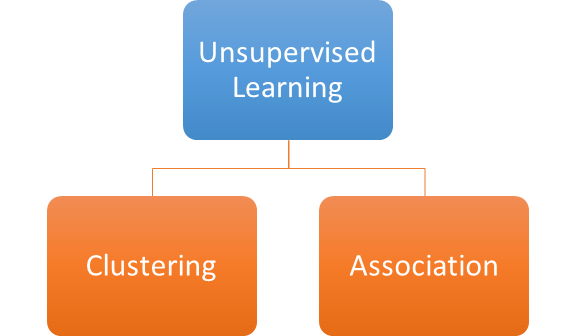
- Clustering : Discovers groups/clusters from a provided data set. Example : new music genre, unknown customer types based on purchasing patterns etc. K- Means algorithm is a common type of clustering algorithm.
- Association : Discover rules/ associations in the data set to help make decisions. Like this section of customers would purchase the product Y would also purchase the product Z. Common association algorithm is the Apriori algorithm for rule based learning.
Summary

The information you have posted is very useful. Thanks for sharing such an informative post.
360DigiTMG
LikeLike